
NOAA originally published this article on June 21, 2022.
Rocket launches affect Earth’s ozone layer
Projected growth in rocket launches for space tourism, moon landings, and perhaps travel to Mars have many dreaming of a new era of space exploration. But a NOAA study suggests that a significant boost in spaceflight activity might damage the protective ozone layer on the one planet where we live.
Kerosene-burning rocket engines widely used by the global launch industry emit exhaust containing black carbon, or soot. This exhaust goes directly into Earth’s stratosphere, where a layer of ozone protects all living things on our world from the harmful impacts of ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Too much of this radiation can cause skin cancer and weakened immune systems in humans. It can also disrupt agriculture and ecosystems.
According to new NOAA research published June 1, 2022, in the in peer-reviewed Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, a 10-fold increase in hydrocarbon-fueled launches would damage the ozone layer and change atmospheric circulation patterns. This level of increase is plausible within the next two decades, based on recent trends in space traffic growth.
Christopher Maloney of the Boulder-based research group CIRES is lead author of the new research. He said:
We need to learn more about the potential impact of hydrocarbon-burning engines on the stratosphere and on the climate at the surface of the Earth. With further research, we should be able to better understand the relative impacts of different rocket types on climate and ozone.
Launch rates have tripled
Maloney said launch rates have more than tripled in recent decades. He said accelerated growth is anticipated in the coming decades. Rockets are the only direct source of human-produced aerosol pollution above the troposphere, the lowest region of the atmosphere, which extends to a height of about 4 to 6 miles (6.5 to 9.5 km) above the Earth’s surface.
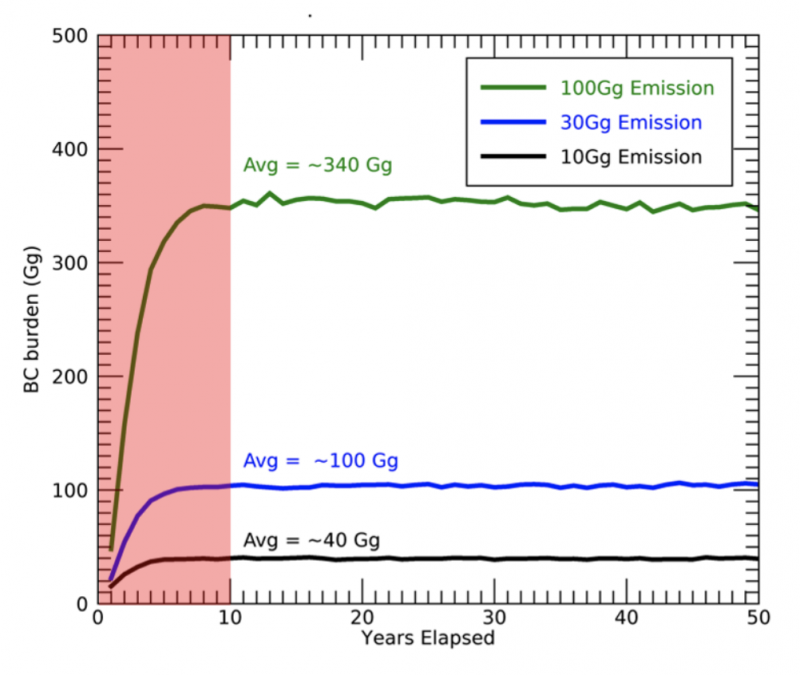
The research team used a climate model to simulate the impact of approximately 10,000 metric tons of soot pollution injected into the stratosphere over the Northern Hemisphere every year for 50 years. Currently, an estimated 1,000 tons of rocket soot exhaust are emitted annually. The researchers caution that the exact amounts of soot emitted by the different hydrocarbon-fueled engines used around the globe are poorly understood.
The researchers found that this level of activity would increase annual temperatures in the stratosphere by 0.5 to 2° Celsius (or approximately 1° to 4° Fahrenheit), which would change global circulation patterns by slowing the subtropical jet streams as much as 3.5% and weakening the stratospheric overturning circulation.
How rocket exhaust affects the ozone layer
Temperature and atmospheric circulation strongly influence stratospheric ozone, noted co-author Robert Portmann, a research physicist with the Chemical Sciences Laboratory, so it was no surprise to the research team that the model found changes in stratospheric temperatures and winds also caused changes in the abundance of ozone.
The scientists found ozone reductions occurred poleward of 30 degrees north, or roughly the latitude of Houston, in nearly all months of the year. The maximum reduction of 4% occurred at the North Pole in June. All other locations north of 30° N experienced at least some reduced ozone throughout the year. This spatial pattern of ozone loss directly coincides with the modeled distribution of black carbon and the warming associated with it. Maloney said:
The bottom line is projected increases in rocket launches could expose people in the Northern Hemisphere to increased harmful UV radiation.
The research team also simulated two larger emission scenarios of 30,000 and 100,000 tons of soot pollution per year to better understand the impacts of an extremely large increase in future space travel using hydrocarbon-fueled engines. They wanted to more clearly investigate the feedbacks that determine the atmosphere’s response. Results showed that the stratosphere is sensitive to relatively modest black-carbon injections. The larger emission simulations showed similar, yet more severe disruptions of atmospheric circulation and climate loss than the 10,000-metric-ton case.
Building a research foundation
The study built on previous research by members of the author team. A 2010 study led by co-author Martin Ross, a scientist with The Aerospace Corporation, first explored the climate impact of an increase in soot-producing rocket launches. A second study performed at NOAA in 2017, on which Ross was a co-author, examined the climate response to water vapor emissions from a proposed reusable space launch system utilizing cleaner hydrogen-fueled rockets. Ross said:
Our work emphasizes the importance of ozone depletion caused by soot particles emitted by liquid-fueled rockets. These simulations change the long-held belief that spaceflight’s only threat to the ozone layer was from solid-fueled rockets. We’ve shown that particles are where the action is for spaceflight’s impacts.
While the new research describes the influence that soot in rocket exhaust has on the climate and composition of the stratosphere, the scientists said it represents an initial step in understanding the spectrum of impacts on the stratosphere from increased space flight.
They said they’ll need to evaluate combustion emissions from the different rocket types. Soot and other particles generated by satellites burning up when they fall out of orbit is also a growing, poorly understood source of emissions in the middle-to-upper atmosphere. These and other topics will need further research to produce a complete picture of space-industry emissions and their impacts on Earth’s climate and ozone.
Bottom line: A new study by NOAA says that with the increase in rocket launches over the next 20 years, the black carbon, or soot, emitted from these launches could damage the ozone layer.
Source: The Climate and Ozone Impacts of Black Carbon Emissions From Global Rocket Launches
Read more: Possible new threat to Earth’s ozone layer
The post Ozone layer damage due to rocket launches? first appeared on EarthSky.
0 Commentaires