How do astronomers know distances to stars?
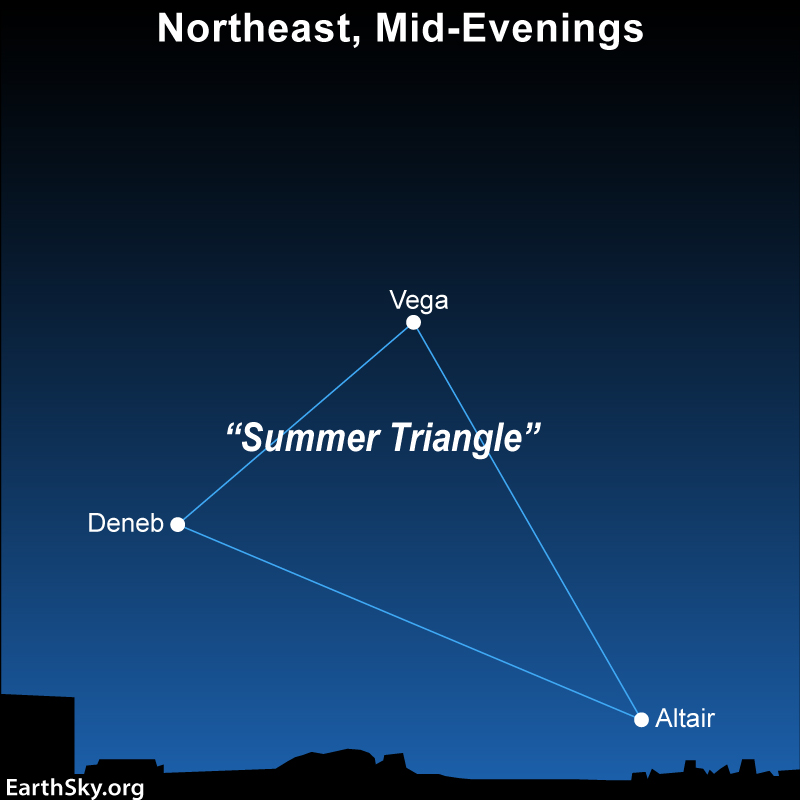
Here is the beautiful Summer Triangle, now about to come back into convenient evening view for another season. An asterism such as the Summer Triangle isn’t a constellation. It’s just a recognizable group of stars. This one consists of three bright stars in three different constellations. Now notice the star Deneb, one of the three Summer Triangle stars. When you gaze at Deneb, you’re gazing across a great distance of space. The exact distance to Deneb is not known for certain, but the currently accepted distance is around 2,600 light-years. Therefore, Deneb is one of the most distant stars we can see with the eye alone.
In fact, however, estimates vary for this star’s distance. The answer is a glimpse into the process of science, and the way that different astronomers or teams of astronomers – using advancing technologies – try to improve on what was learned earlier, sometimes many years before.
Divining the distance to Deneb
Scientists obtain estimates for Deneb’s distance through a variety of methods. Some of these methods involve theoretical models related to the way stars evolve, and some assume Deneb’s membership in the Cygnus OB7 association of stars. (Cygnus OB7 is a star-forming complex in the Milky Way.)
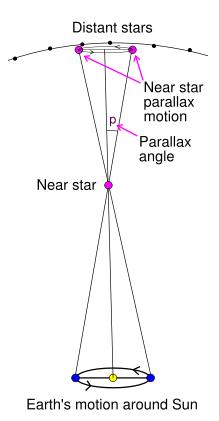
ESA’s Earth-orbiting Hipparcos Space Astrometry Mission provided the most important modern distant measurement for Deneb in the 1990s. Hipparcos gathered astrometric data on Deneb. Early analyses of the data indicated a distance of somewhere around 2,600 light-years.
Since then, various groups of astronomers have re-analyzed Hipparcos data. Consider that computer power, which gets stronger with each passing year, helps to improve techniques for analysis. For example, the peer-reviewed journal Astronomy and Astrophysics published a 2009 study using a newer method of analysis. This analysis showed a distance for Deneb that’s barely half the widely accepted value.
What distance reveals
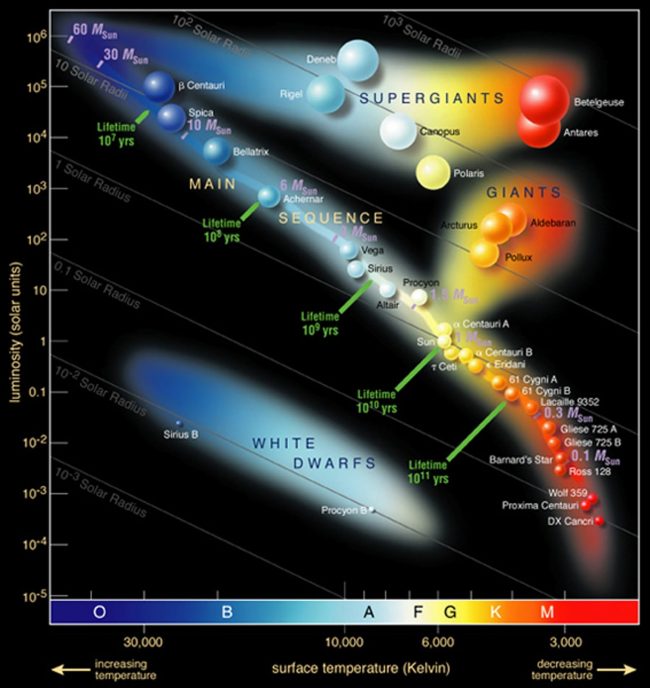
Why does Deneb’s distance matter? It matters to astronomers because – if they don’t know exactly how far away the star is – they can’t get accurate numbers of its true size, mass and energy output.
ESA has another astrometric satellite – called Gaia – that orbits around Earth. It measures the positions and distances of stars with more precision than ever before, and it’s in the process of constructing what ESA says will be:
… the largest and most precise 3D-space catalog ever made.
Unfortunately for those studying Deneb, Gaia can’t get an accurate read on the star because it’s too bright for Gaia’s sensitive instruments. Deneb is so bright that it remains mysterious, even across great distances.
Bottom line: The star Deneb – part of the famous Summer Triangle – is one of the most distant stars you can see with your eye alone. Why don’t we know its distance precisely?
Read more: Delta Cephei helps measure cosmic distances
The post Deneb: How astronomers know how far away it is first appeared on EarthSky.
0 Commentaires