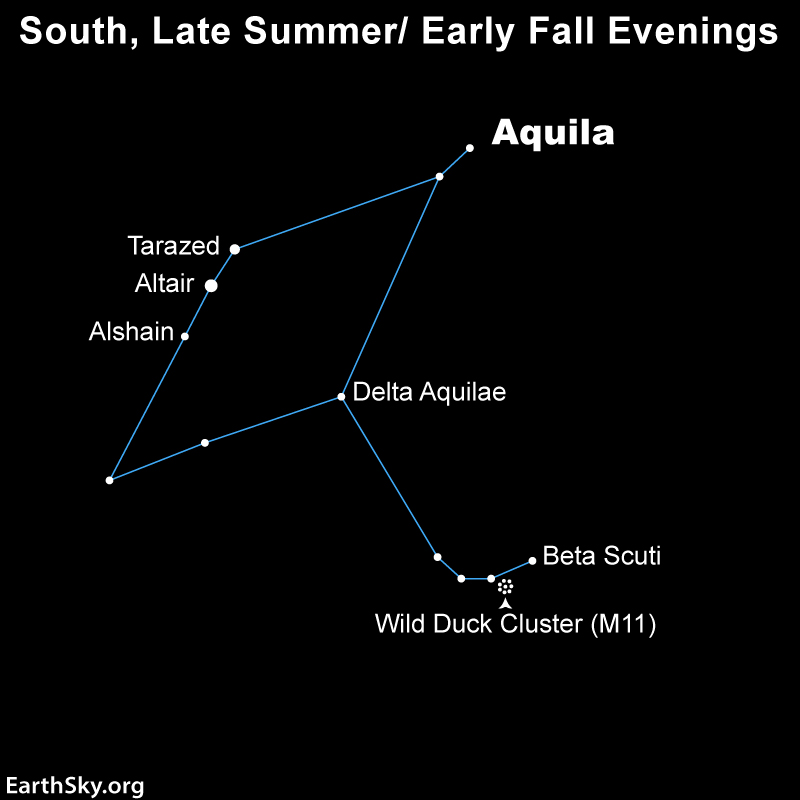
The best time to see the constellation of Aquila the Eagle in the Northern Hemisphere is in late summer and early fall as it soars along the Milky Way. Because our galaxy provides a starry backdrop, many clusters and nebulae lie within its borders. Aquila’s brightest star, Altair, is the southernmost corner star in the Summer Triangle. In mythology, Aquila carried Zeus’s thunderbolts for him.
The stars of Aquila the Eagle
The brightest star in Aquila is Alpha Aquilae, or Altair. At magnitude 0.76, it is one of the three bright stars that mark the corners of the Summer Triangle. Deneb and Vega are the other two and they lie higher in the sky, closer to the zenith on summer evenings. Altair lies just 17 light-years away from Earth.
Two moderately bright stars lie on either side of Altair. To the southeast is Beta Aquilae, or Alshain. This magnitude 3.71 star lies 45 light-years away. To the other side of Altair is Gamma Aquilae, or Tarazed. At magnitude 2.72, it’s brighter than Alshain but lies much farther away at 460 light-years. These stars are usually considered the tail feathers of the Eagle.
The star marking Aquila’s back is Delta Aquilae, at magnitude 3.36 and 50 light-years away. Theta Aquilae marks the wing that points to the east-southeast. It shines at magnitude 3.26 from across 286 light-years. The wing that points to the north (and Vega) holds Zeta Aquilae at magnitude 2.99 and 83 light-years distant. The star that marks the head of the Eagle is Lambda Aquilae at magnitude 3.43, lying 125 light-years away.
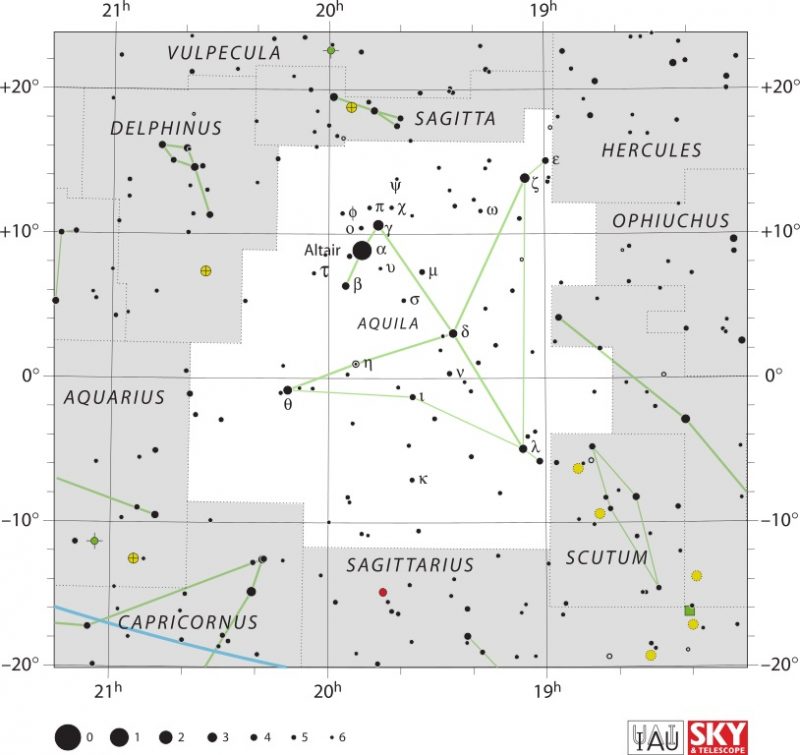
Clusters in Aquila
While there are no Messier objects in Aquila, there is still a lot to see, especially if you have a big enough telescope. Two globular clusters lie in Aquila: NGC 6749 and NGC 6760.
The two globular clusters are northwest of a line drawn between Delta Aquilae (the back) and Lambda Aquilae (the head). Closest to that line is NGC 6760, which shines at magnitude 9.1. About two degrees farther away is NGC 6749 at magnitude 11.1.
Several open clusters lie in Aquila, but most of them are faint. The best one to observe is NGC 6755, a 7.5-magnitude grouping found northwest of the star marking the back of the Eagle. Another good open cluster to try for is NGC 6709, which, at magnitude 6.7, appears in binoculars. NGC 6709 is about five degrees southwest of Zeta Aquilae, the upper wing of the Eagle. In between these two points is yet another cluster, NGC 6738. This sparse cluster is 8th magnitude.
A lot of observers who come to Aquila use it to starhop to a cluster just over the border in Scutum. The Wild Duck Cluster, M11, shines at magnitude 6.3, making it brighter than any clusters in Aquila. Here’s how to find it.
Nebulae of Aquila
A number of nebulae lie along the line that marks the body of the Eagle, but only one is bright enough to reach even 10th magnitude. NGC 6790 lies a little less than two degrees from the star that marks the back of the Eagle in the direction of its head.
Good luck tracking down these tough-to-spot, faint objects in Aquila the Eagle. You can always just scan the area in binoculars and see what materializes.
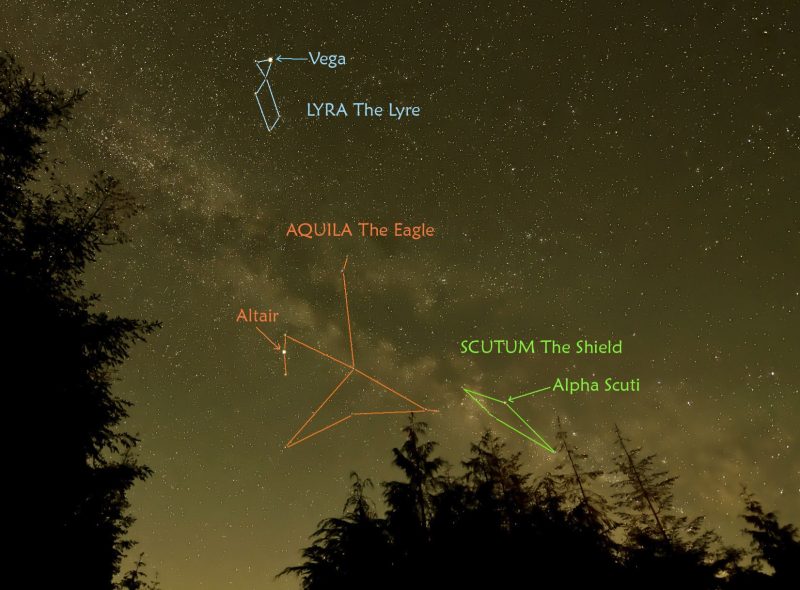
Bottom line: Aquila the Eagle is home to the bright star Altair, which forms one corner in the Summer Triangle. You can see this constellation at its best on northern late summer or early fall evenings.
The post Aquila the Eagle soars along the Milky Way first appeared on EarthSky.
0 Commentaires