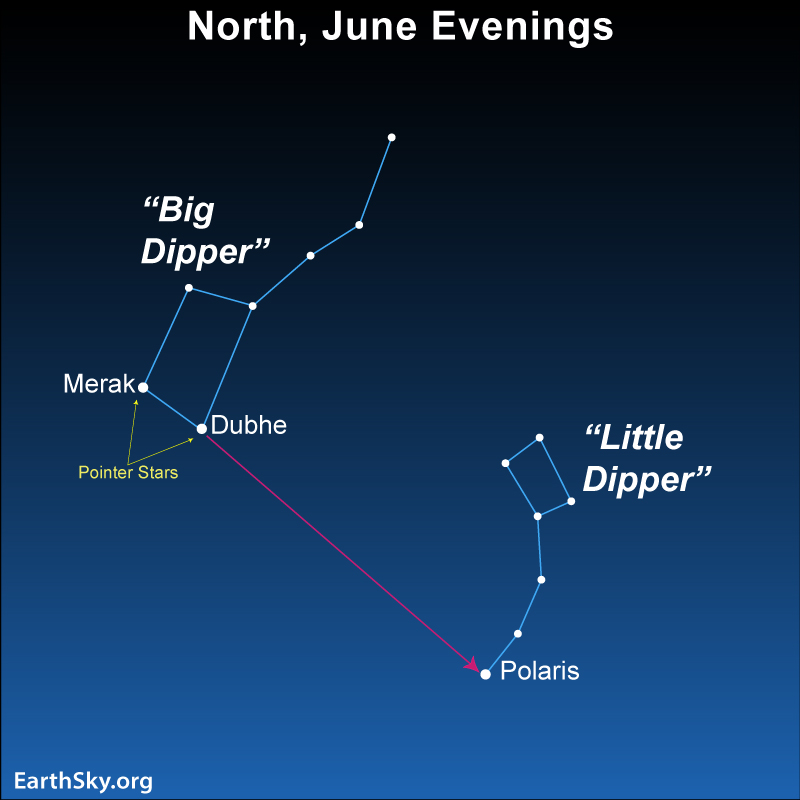
Tonight, assuming you’re in the Northern Hemisphere, you can easily find the legendary Big Dipper, called The Plough by our friends in the U.K. or The Wagon throughout much of Europe. This familiar star pattern is high in the north at nightfall in June. Find it, and let it be your guide to the Little Dipper, too.
You can find the Big Dipper easily because its shape really resembles a dipper. Meanwhile, the Little Dipper isn’t as easy to find. You need a dark sky to see the Little Dipper, so be sure to avoid city lights.
How to find the Dippers
Assuming you’re in the Northern Hemisphere, simply face northward on a June evening and watch for a large dipper-like pattern. Which way is north? Rotate around until your left side faces the sunset point. You are now looking toward the north. That easy-to-see pattern high in the sky will be the Big Dipper. Notice that the Big Dipper has two parts: a bowl and a handle. The bowl has four stars, and the handle has three. See the two outer stars in the bowl? They’re known as The Pointers because they point to the North Star, which is also known as Polaris.
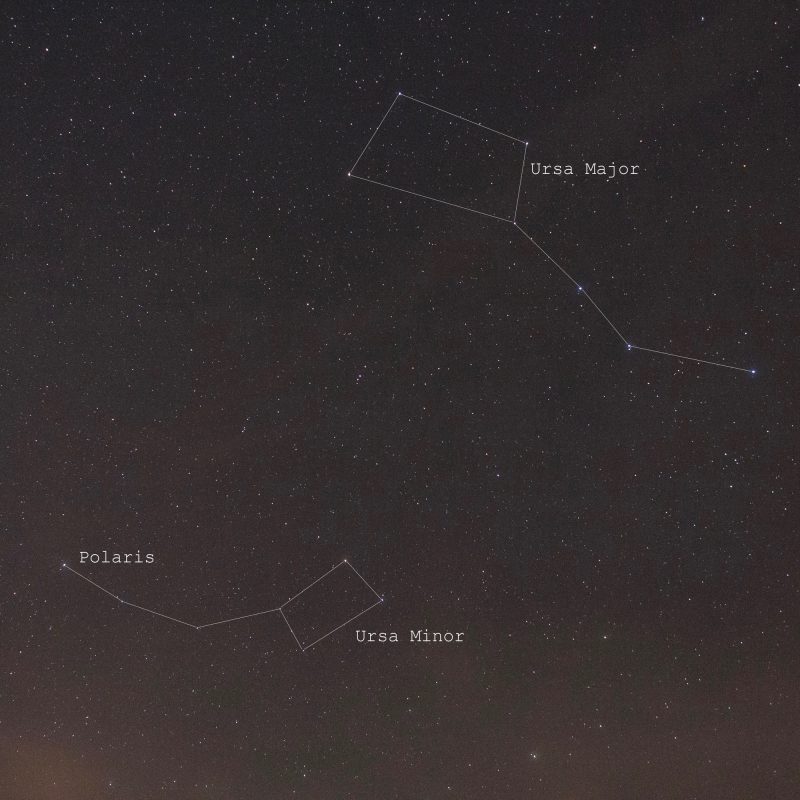


Polaris is the brightest star of the Little Dipper
Once you’ve found Polaris, you can find the Little Dipper. Polaris marks the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. You need a dark night to see the Little Dipper in full, because it’s so much fainter than its larger and brighter counterpart. If your skies are not really dark, you might be able to trace out only the three brightest stars in the Little Dipper.
By the way, can you see the Big Dipper from Earth’s Southern Hemisphere? Yes, if you’re in the southern tropics. Much farther south, and it gets harder because as you go southward on Earth’s globe, the Dipper sinks closer and closer to the northern horizon.
Meanwhile, Polaris, the North Star, disappears beneath the horizon once you get south of the Earth’s equator.
Big and Little Dipper in skylore
In his classic book Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning, Richard Hinckley Allen claims the Greek constellation Ursa Minor was never mentioned in the literary works of Homer (9th century BCE) or Hesiod (8th century BCE). That’s probably because this constellation hadn’t been invented yet.
According to the Greek geographer and historian Strabo (63 BCE to about 21 CE), the seven stars we see today as part of Ursa Minor (the Little Dipper) didn’t carry that name until 600 BCE or so. Before that time, people saw this group of stars outlining the wings of the constellation Draco the Dragon.
When the seafaring Phoenicians visited the Greek philosopher Thales around 600 BCE, they showed him how to navigate by the stars. Purportedly, Thales clipped the Dragon’s wings to create a new constellation, possibly because this new way of looking at the stars enabled Greek sailors to more easily locate the north celestial pole.
But it’s not just our names for things in the sky that change. The sky itself changes, too. In our day, Polaris closely marks the north celestial pole in the sky. In 600 BCE – thanks to the motion of precession – the stars Kochab and Pherkad more closely marked the position of the north celestial pole.
Read more: Kochab and Pherkad: Guardians of the Pole
Bottom line: Look for the Big and Little Dippers in the north at nightfall on June evenings.
EarthSky astronomy kits are perfect for beginners. Order today from the EarthSky store
The post Big and Little Dippers on June evenings first appeared on EarthSky.
0 Commentaires